Thermal mass flow meters are frequently utilized in the process of measuring low gas fluxes; nevertheless, what precisely are these meters? And how do these particular devices differ from many other gas flow meters that are available?
You might also find it useful to learn about the many types of flow sensors as well as the benefits and drawbacks associated with each.
Comparing Measurements Of Mass And Volume Flow
It has been shown that mass, not volume, is the most essential variable in many industrial and scientific operations. Due to the impact that temperature changes or pressure have on the density of a constant volume of gas, volumetric flow measurements are not as trustworthy as mass flow measurements.
This is because mass flow measurements do not take temperature or pressure into account. Check out this link to find out more https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Thermal_mass_flow_meter.
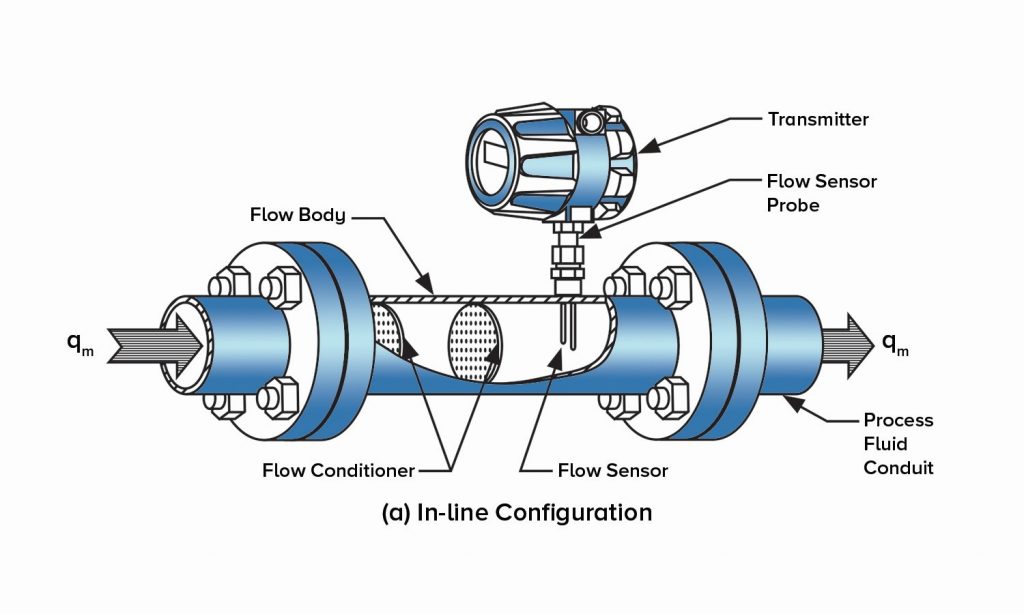
Thermal mass flow meter, in contrast to volumetric flow measuring devices like purge meters and turbine meters, are unaffected by shifts in the temperature or pressure of the flow that is being measured. The mass flow meter is capable of providing direct measurements of the flow of mass.
The vast majority of alternative approaches compute density and flow by measuring volumetric flow first, followed by independent measurements of temperature and pressure intoetermine mass flow.
Because they detect the flow on a molecular level, mass flow meter arcanive you a delivery of gas that is exceptionally accurate, consistent, and dependable.
How Do Thermal Mass Flowmeters Measure The Flow Of Fluid?
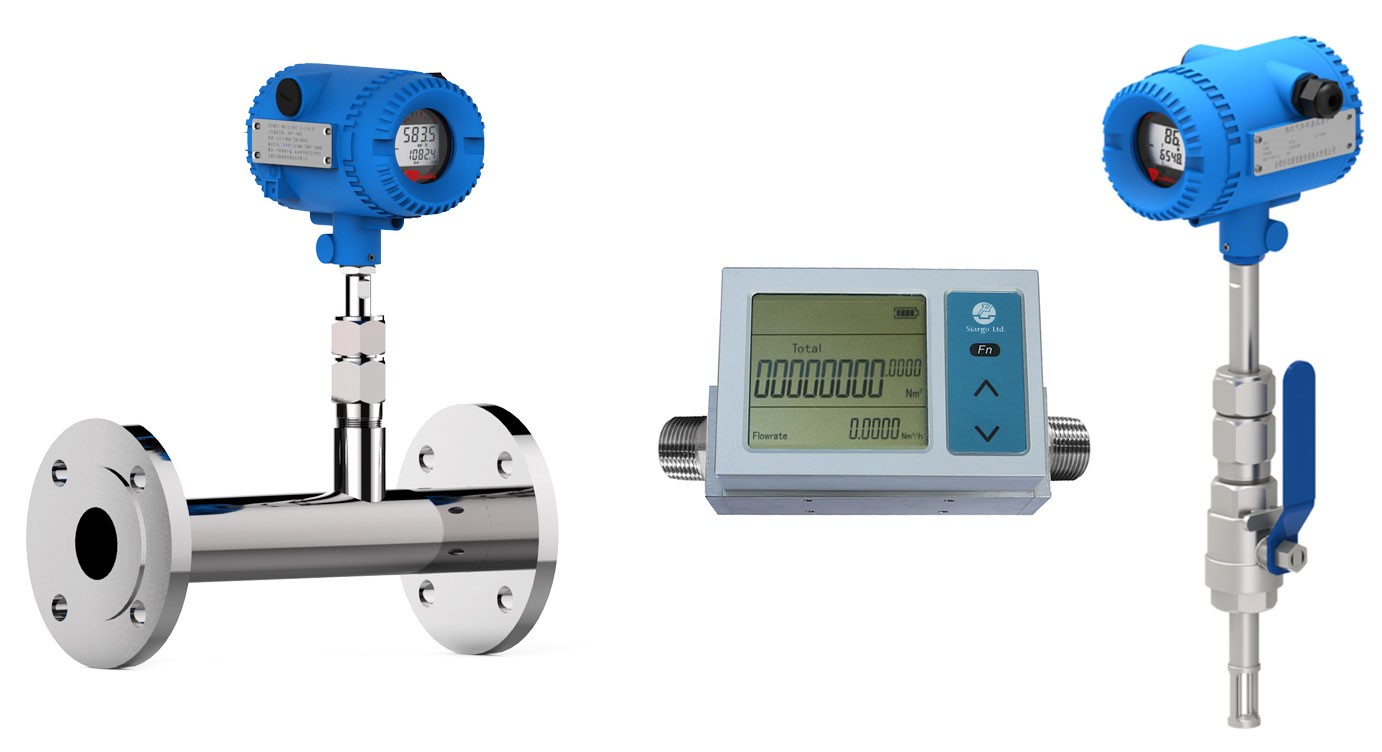
Convective heat transfer is used as the basis for the measurement of gas flow by the thermal mass meter. Both insertion- and inline-style flow bodies are offered by Sage as potential configurations for the flow meters. In either scenario, the probe of the meter is inserted into the gas stream that is flowing via a stack, pipe, or duct.
Two sensors, also known as resistance temperature detectors (RTDs) or thermometers that measure temperature using resistance, may be found toward the end of the probe that extends from the meter.
The RTDs are made up of windings made of robust reference-grade platinum that are encased in a protective sheath made of 316 stainless steel or Hastelloy C.
One RTD is preheated by an integrated circuit and operates as the flow sensor, while the temperature of the gas is determined by a second RTD that functions as the reference sensor and acts as the flow sensor.
Between the flow detectors and the reference detectors, the Sage patented circuitry ensures that there is always an overheating condition. Read more here.
As the gas moves past the heated RTD, floating gas molecules carry away the heat from it. As a consequence, the sensor cools down, and the energy is lost.
When this happens, the equilibrium of the circuit is thrown off, and the temperature differential (T) that exists between the heated RTD and the reference RTD shifts.
Within one second, the circuit is able to return the energy that was lost by heating the flow detector in order to correct the temperature of the overheat.
The amount of electrical power that must be maintained in order for this overheating to continue is the mass flow signal.
The Benefits Of Measuring Thermal Mass Flow:
When it comes to determining the mass flow of low gas flow, thermal mass flow meter is unquestionably the most common type of instrument used. Since they were first introduced in the middle of the 1970s, these instruments have undergone significant development.
They have gone from being analog to digital, from having a low flow to a higher flow, as well as from having applications in machines and laboratories to applications in industrial environments and sometimes even hazardous areas.
There’s a thermal mass flow meter available to meet the requirements of virtually any low-flow gas application. Measurement based on the concept of Coriolis flow and measuring based on differential pressure is two more measurement philosophies that arapplyo situations using low-flow gas.
Coriolis flow measuring
Whenever measuring supercritical gases and then when users wish to measure the mass flow of variable or unknown gas combinations, users can benefit from using mass flow meter based on the Coriolis principle, which offers benefits.
Differential pressure measuring
In the case of differential pressure measurement, the recorded delta-p is transformed to mass flow by the application of a computation that takes into account the temperature of the gas being measured in addition to the density and dynamic viscosity of the gas being measured.
When compared to this approach, thermal sensors are less susceptible to pressure variations in your operation, and the conversion for many other gases in a thermal flowmeter is inherently more precise. In addition, thermal sensors have a shorter response time.
Read Also: