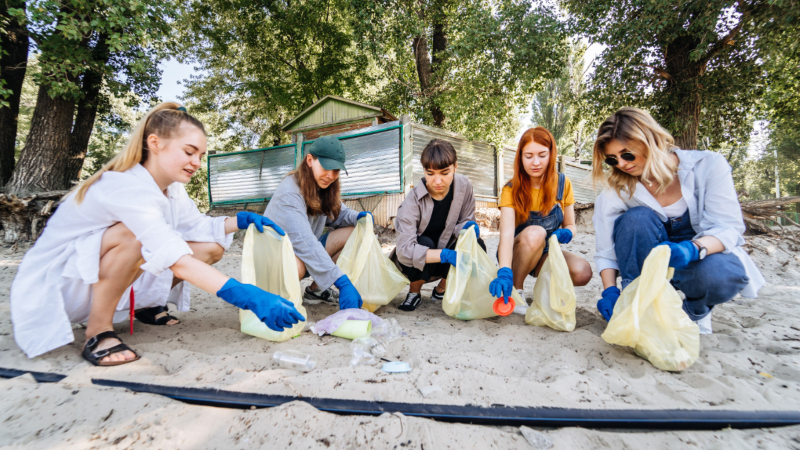
Living in a community isn’t just waving hello at your neighbor once in a blue moon; it’s teaming up, pitching in, and, if we’re being totally honest, diving into the messes that creep up when no one’s looking. A clean place to live? Everyone wants that, but it’s easy to forget the magic happens when folks actually roll up their sleeves together.
So—you’re wondering how to transform your block, or maybe the whole neighborhood, from “kinda grimy” to “hey, this feels good?” Well, you’re in luck. Find a comfy spot, grab a snack, and let’s stumble through this guide that’ll show you how to kick off a wild, lively clean-up with real neighborhood spirit—and maybe a few laughs (or groans) along the way.
Plan The Event
Start with picking a date that isn’t smack in the middle of hurricane season (learned that one the hard way). Most people will show up if it’s sunny and relaxing. Just ask around—everyone’s got opinions, but don’t let ‘em bother you.
Next, go for a wander. Scope out places clinging to old fast-food wrappers and mystery stains: playgrounds that look unloved, church steps that birds seem to love, run-down spots near a start-up café, or that strip mall where the wind always stirs up trouble. If you spot somewhere desperate for TLC, circle back and keep it on your radar.
Gather Supplies
Get your hands on those big, sturdy trash bags—thin ones split and spill all over, and trust me, your shoes will hold a grudge. Decent gloves matter, unless you like “the feel” of wet leaves. Mark out recycling, compost, straight-up trash bins (maybe with neon stickers).
Bonus points if you show up with snacks. Water bottles, juice boxes, apples, whatever—hungry helpers get cranky and wander off, so don’t skimp on refreshments! Even gummy bears… sometimes folks battle over the last packet.
Promote The Event
You want some buzz? Blast out the news on whatever platform people read: Instagram, group texts, those ancient bulletin boards with tattered flyers. Toss a poster in the local diner or drag a friend into posting for their book club.
Don’t be shy about nudging the bakery owner or the dog groomer down the street—local businesses actually love showing off their good side. Invite them to pitch in, toss in supplies, or sponsor snacks. Makes it easier for everyone.
Recruit Volunteers And Professionals
You won’t get far by flying solo. Boot up some group texts, ask the weird old guy who walks his cat, holler at teenagers hanging out after school.
Keep it simple: scribble names on a sheet, get their favorite snacks, maybe ask about allergies (trust me on that one).
Some spots, like big medical offices or churches, need more than elbow grease. If you’re all based in Florida, and you’ve got a church that’s too daunting for DIY, don’t sweat it; call in a Florida service company that cleans churches and let them deal with the deep grime. Sometimes you gotta leave it to the pros.
Conduct The Clean-Up
On event day, show up a bit early (but not too early—coffee first). Lay out trash bags, hand stuff out, and give every person a quick “you got this!” handshake.
Safety rules? Yeah, mention those—no running with sharp sticks, careful with broken glass. Sketch out who’s tackling what area, and let teams shuffle around if they feel like it.
Most important: let people go at their own speed. Nobody likes barking orders before noon.
Dispose Of Waste Properly
When your crew’s done wrangling trash, split the loot. Real junk goes to plain trash, bottles and cans to recycling, orange peels to compost; unless someone gets creative with “compostable” pizza boxes. Hazardous stuff? Don’t just toss it—it needs special care, and sometimes you gotta make a couple calls before someone picks it up.
Celebrate And Thank Volunteers
After the last bag’s tied up, don’t just disappear. Line up some cookies, crank a playlist, take “before and after” pics (so people believe you actually cleaned up).
Thank whoever showed; handwritten notes go far, but jokes work too. Show off your progress, brag a little, and let everyone enjoy that glow of “wow, look what we did.” You’d be surprised how much it boosts everyone’s confidence and makes ‘em keen for next time.
Final WordsIt’s wild how these little clean-ups add up—you blink, suddenly half the block’s looking better than it did last month. Stick with it, loop people in for the next round, maybe make it a tradition. Set a day each month for some good-natured chaos.
With a smidge of determination (and maybe one too many group texts), you’ll end up with a cleaner, happier community—and a story or two to laugh about over coffee.
Read Also:
- 5 Hotel Housekeeping Tricks You Need To Clean Your Bathroom
- Transform Your Office: Why A Clean Workplace Is A Game Changer
- Finding the Perfect Fit: A Landlord’s Guide to Selecting Suitable Tenant