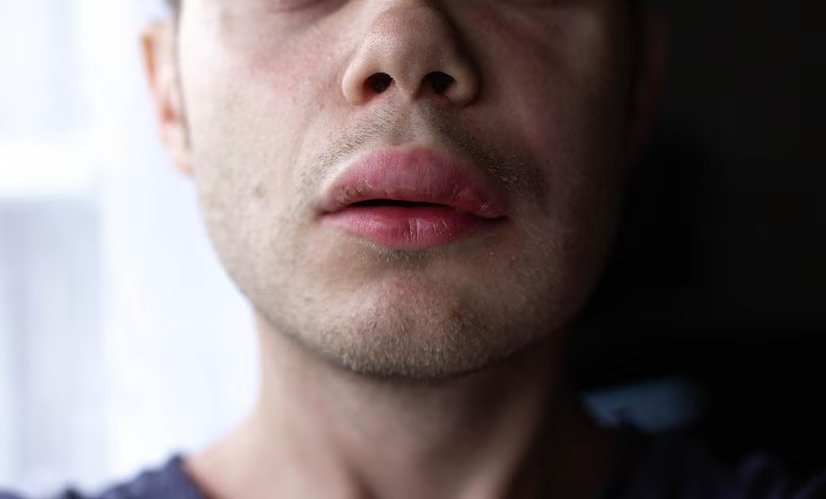
Angioedema is a medical condition characterized by sudden swelling beneath the skin. We aim to equip readers with a comprehensive understanding of the available options, ranging from medications to lifestyle modifications and emergency care. Whether you are a healthcare professional seeking to expand your knowledge or an individual searching for effective management strategies, this guide will be invaluable.
Common Treatments for Angioedema
Antihistamines, such as Benadryl or Zyrtec, are often the first line of defense and can help reduce symptoms by blocking the release of histamine, a substance responsible for swelling. Corticosteroids like prednisone are prescribed to reduce inflammation and relieve symptoms. In more severe cases, epinephrine may be administered to rapidly reduce swelling, particularly in angioedema triggered by an allergic reaction. However, it’s important to note that medication alone may not be sufficient to manage angioedema, and other treatment options may be necessary.
In cases where allergens trigger the condition, identifying and avoiding these triggers is crucial to prevent future episodes. Some individuals may benefit from allergen immunotherapy, a long-term treatment that gradually reduces sensitivity to specific allergens. In more severe and recurrent cases of angioedema, a specialist may recommend using C1 esterase inhibitor replacement, which can help prevent swelling attacks.
How Lifestyle Changes Complement Angioedema Treatment
Lifestyle changes can significantly complement angioedema treatment and help individuals manage their symptoms more effectively. One crucial lifestyle change is identifying and avoiding triggers that can cause angioedema episodes. These triggers can vary from person to person but may include certain foods, medications, insect bites, or environmental factors such as extreme temperatures or stress.
Another necessary lifestyle change is to adopt a healthy diet and maintain a healthy weight. Eating a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins can boost the immune system and reduce inflammation, which may help prevent angioedema episodes. Additionally, maintaining a healthy weight can reduce the strain on the body and improve overall health, potentially reducing the risk of angioedema.
Managing stress levels is also crucial in complementing angioedema treatment. Stress can be a trigger for angioedema episodes and can exacerbate symptoms. Engaging in stress-reducing activities such as meditation, exercise, or practicing mindfulness techniques can help individuals manage their stress levels and prevent flare-ups of angioedema.

When to Seek Medical Help for Angioedema
While mild cases of angioedema may resolve independently without medical intervention, sure signs should not be ignored. If the swelling affects the throat or causes difficulty breathing or swallowing, immediate medical attention should be sought. This is because angioedema involving the throat can lead to a potentially life-threatening condition known as anaphylaxis.
Prompt medical attention is crucial when angioedema involves the throat, causes breathing difficulties, or is accompanied by severe pain, fever, or a rash. By seeking medical help promptly, individuals can receive the necessary treatment and management strategies to deal with angioedema and its potential complications effectively.
Living with Angioedema: Long-Term Management Strategies
One key aspect of managing angioedema is identifying and avoiding triggers that may induce an episode. Common triggers include certain foods, medications, environmental factors, and stress. Keeping a detailed diary and working closely with a healthcare professional can help identify specific triggers and develop an individualized management plan.
In addition to trigger avoidance, medication is often necessary for long-term management of angioedema. Antihistamines, such as cetirizine or loratadine, are commonly prescribed to help minimize the release of histamine and reduce swelling. In cases where antihistamines are insufficient, corticosteroids or other immunosuppressive medications may be prescribed to control inflammation and prevent swelling.
Individuals living with angioedema should also be prepared for emergencies. It is essential to always carry an epinephrine auto-injector for immediate use in case of severe swelling that may lead to anaphylaxis. An emergency action plan should be in place, detailing the signs and symptoms of a severe attack and the steps to take, including when to administer the epinephrine auto-injector and when to seek immediate medical assistance.
Read Also: