Of all techniques and methods used to join surfaces, metal sheets, Iron, and other objects together, soldering is highly preferred because it does not cause any type of damage to the items being joined together. This is because the solder used to stick them together has a lower melting point than most metals and it offers durable yet reversible bonds between the items. In addition to that, although there are a few key differences between the two types of soldering gear used, they share a similar trait and they’re both easily operable, which we will discover more in this article
What Is Soldering?
There are several types of soldering using different filler metals called solder, but, they all use the same concept which is heating a filler metal between two items so that it melts and fills the seam between the two items.
Soldering is done using either individually bought soldering gear, which allows you to choose the type of tool that is most suitable for the project you are planning to work on, or a soldering station which usually is a standard combination of a soldering iron and a power supply.
Soldering Iron
In order to learn how to use a soldering iron, one must first know its basic parts and the science behind its mode of operation.
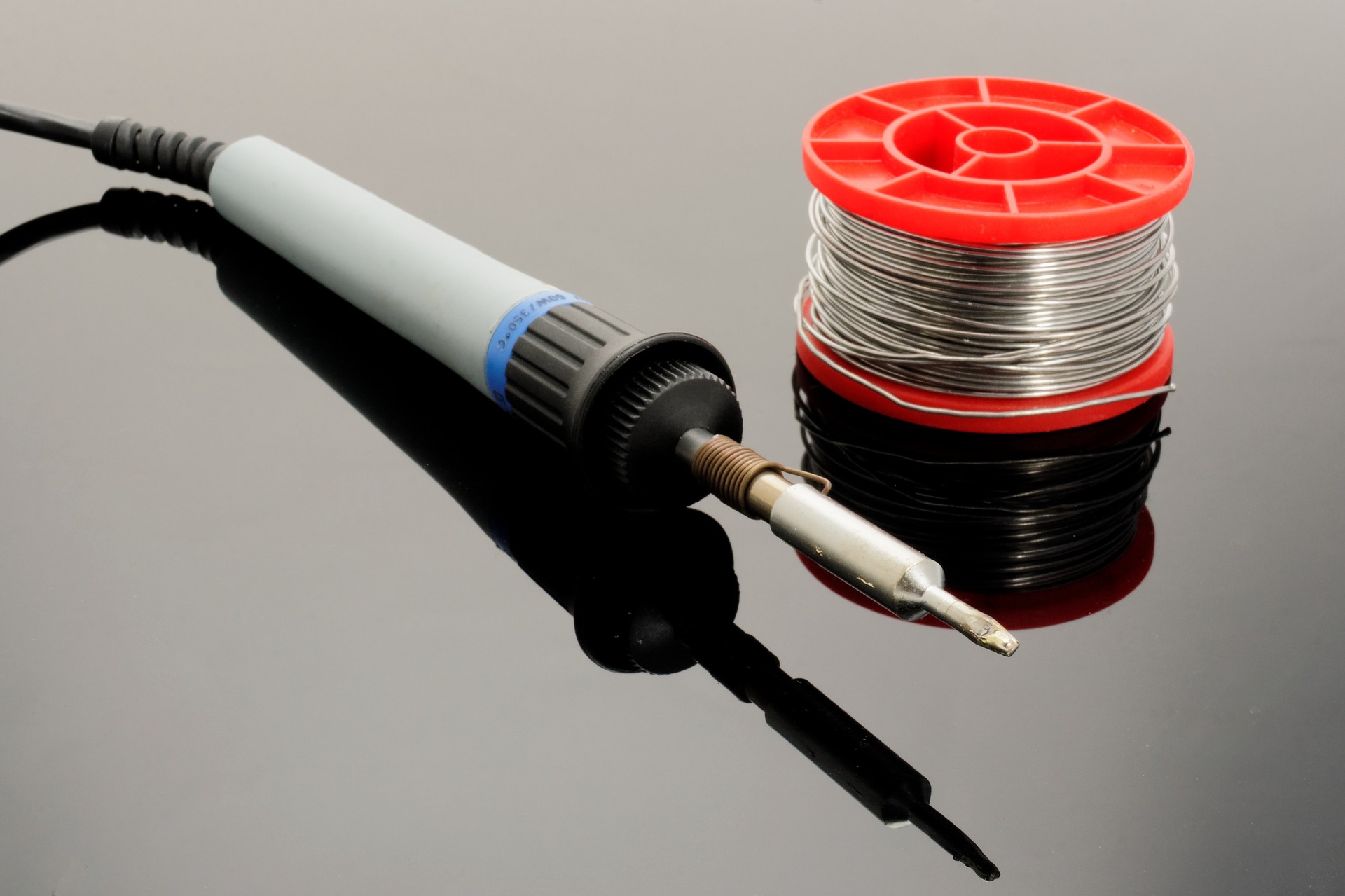
It is simply a tool that connects to a power supply, it consists of a handle that doesn’t conduct heat and a tip that heats up very quickly to high temperatures so it can melt the solder, it also cools down fast.
To Be More Specific, The Main Parts Of Soldering Iron Are:
- Soldering tip: All soldering irons contain iron tips which are the only part that heats up; it doesn’t ooze out the solder as most people think, it simply heats the metals being joined so that when the solder is applied, it melts, but more often than not, the solder would stick on the tip. Luckily, most tips are interchangeable so, you can replace your tip in case of damage or in case you need a specialized tip to suit your uses; bear in mind that tips vary in size and shape, thus, they vary in their uses as well.
- Wand: The wand is the handheld part of the iron that the tip is attached to. It can be made from a large number of materials that poorly conduct heat or isolate it completely so as to prevent heat from the tip from transferring to the part where the wand makes contact with the skin. Inside the wand, there are wires and metal contacts that conduct and convert the electricity from the power outlet to heat. The contradicting functions of a wand are the reason why most people prefer to buy high-quality wands from renowned brands.
Of course, there are other extras and accessories like brass sponges, cradles, and tip tinner which can be purchased individually or found in soldering stations which is actually one of the advantages of soldering stations; but, the two main parts will always remain the tip and the wand.
Step 1: Safety
First of all, before using a soldering iron, you must be familiar with standard safety precautions since the iron tends to get really hot; not to mention the fact that solder is literally molten metal. So, it would be smart of you to wear protective gear such as; safety goggles and protective gloves, because your fingers are most likely to come into contact with the tip during the first few times. You also should keep in mind to tie your hair and avoid wearing loose-fitting clothes. Moreover, it is preferable to work in a well-ventilated area since some types of solder contain lead which produces toxic fumes, it is also important to thoroughly clean your hands after handling lead-based material.
Step 2: Preparing The Tip
The tip should be regularly cleaned of any old solder because when old solder solidifies, it turns into a heat isolator due to oxidization resulting in a totally inefficient and highly wasteful soldering process. Not only that but also, slow heating means that you will have to hold the iron to the items being joined for a longer time; it would be highly inconvenient for you and very damaging for sensitive objects like PCBs.
So, when the iron is fully heated, softly drag the tip against a sponge to remove old solder. You want to aim for a shiny tip. After cleaning the tip, you should “tin” the tip; to make it last longer and conduct heat better through newfound layers of solder. Same as above, on a fully heated iron, apply a little piece of solder and lightly coat the tip with tinner; then, immediately start soldering while cleaning and tinning the tip between every couple of joints for maximum conductivity and efficiency.
Step 3: Actual soldering
With your dominant hand holding the iron and the other holding a piece of solder, touch the area where the object comes into contact with the solder and hold it there for about a second then slide the solder underneath the tip while pushing the solder rod further according to how much solder you need.
Then, make sure to pull back the solder first while holding the tip in position until all the solder melts; it usually takes about five seconds or less. Solder cools down fast so, you will not need to blow on the joint since it will only lead to a weak joint which can be identified by its oxidized, unclear, and grainy appearance. What you want to get is a smooth connection, not a lump.
Finishing touches :
After you’ve had enough soldering for the day, clean and in the tip again before you put it into storage, it helps increase its lifespan.
As you may have noticed, soldering is not that hard of a task, it only requires soldering gear, steady hands, and concentration. So, go ahead, start soldering, and don’t be afraid to get creative.
Read Also: