The use of USB Cable (Universal Serial Bus) has dramatically increased ever since the evolution of cable chargers and file transmission from one gadget to another. It was developed in the late 1990s as a mere connector between computers and external electronic devices. Since then, USB has long been a fundamental power tool for data transmissions, such as songs files, video, photos, and charging of devices and peripheral connections.
If you have been using USB cables for a long time now, you probably noticed that the majority of them are not created equally. What does that mean? One USB cable charges your phone pretty quickly than the other. When all USB cables look quite the same, it’s hard to distinguish which is good.
No need to worry, you’re on the right page. Below are things you need to know to help you identify a good USB cable.
Importance of a Good USB Cable:
It is essential to choose the right USB cable. It creates an impact on the charging process and data transmission of your gadget. If you opt for cheap ones — which come at a cheap price, too — it may result in possible safety risks. We don’t want to ruin our devices because of some low-quality USB cords, don’t we?
The interference plug is not sturdy. It is prone to damage because of overcharging, especially if it is used for a longer period of time. This may lead to future dangers. Therefore, it is of huge importance to know what comprises a good USB cable.
Lower Gauge Charges Faster:
Gauge is the wire thickness of a USB cord; when a gauge is higher, the wire is thinner and charges your device slower. This is something we want to avoid. If you’re looking for a good USB cable, then the gauge is one of the things you need to consider.=
Thick gauge lessens electrical resistance and enables a better electron flow, thus charges your device fast. Moreover, your USB cable length can affect the charging speed of your device. Short and cheap cords may quickly charge your phone or whatever device you have, while longer ones may take longer.
Types of USB Cord:
Generally, there are different specific USB cable types. These are the following:
- Type A – This comes in a rectangular shape and is often seen in media players, computers, televisions, and DC charging cords.
- Type B – This type of USB cable has a connector on the other side which is plugged into external devices, just like with the right angle pin header for a PCB. Type B cables have two sub-types: the micro and the mini. These three have the same functionality but differs in socket shape design.
- Mini-USB – The standard for early portable devices. You can hardly see them today. However, some devices still use this like PlayStation controllers and MP3 players.
- Micro-USB – The more recent standard for several mobile devices, including tablets, smartphones, and video game consoles. They are slowly fading in the industry due to the introduction of the Type-C.
- Type C – This type enables the user for a reverse plug. You can plug your USB cable regardless of what direction, if it is in the negative or positive way without having to worry the cable is upside down.
Appearance:
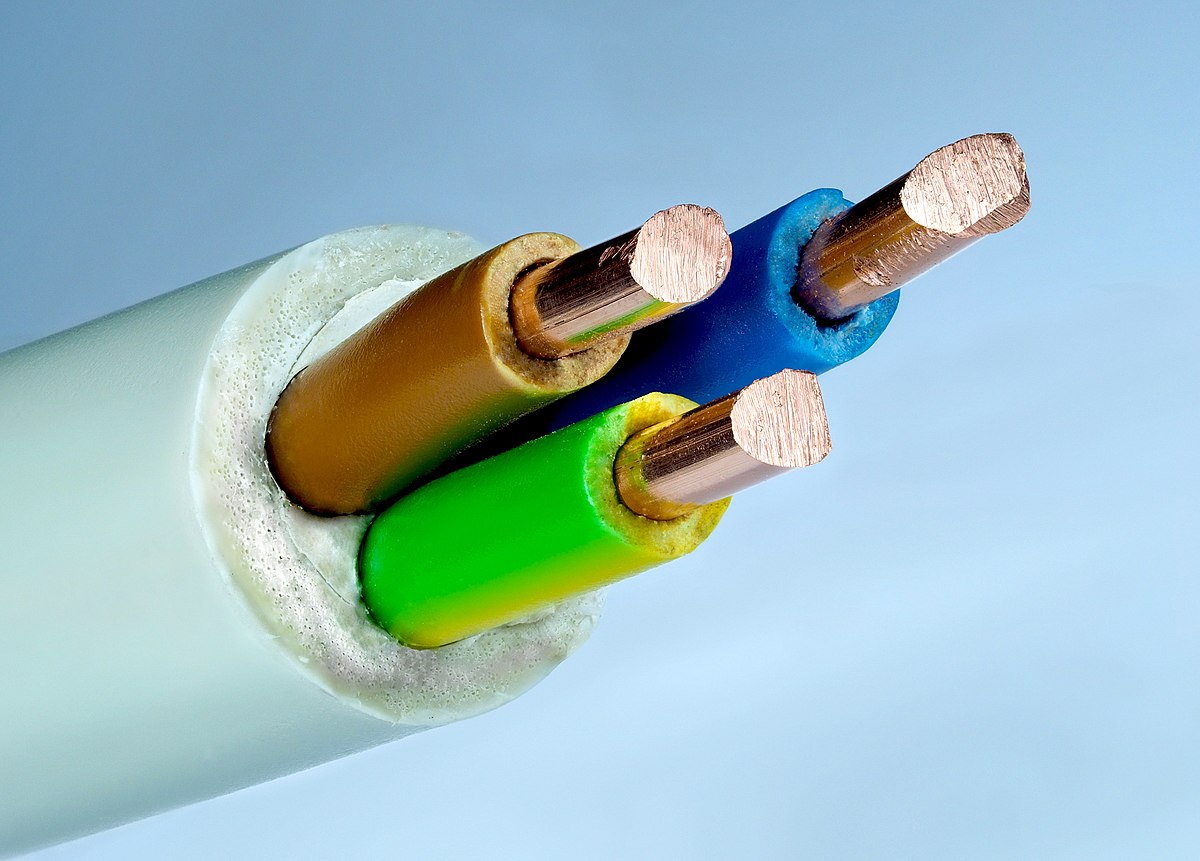
Take note of the entire package detail carefully. You need to remember that, the thicker the gauge is, the higher the strength of tensile is, and the power output is much larger, as well. The entire body cord does not easily get hot, and the thick gauge is perfect for inner copper protection.
Texture:
You can already tell if the USB cable is of great quality or not by knowing its texture through touch. Soft and smooth cable texture means the cable has excellent quality. Hard texture ones are often in low-quality. Also, storing your USB cable will be easier if it is soft and flexible.
Connection:
High-quality USB cables are durable, condensed, soft and the insulation layer is tightly mounted with wire harness. Cheap cables are easy to identify as they are not neatly and properly made.
Copper Core:
A great USB cable comes in the thick and premium quality copper core. Charging of your device will be more stable and efficient since authentic copper core enhances data transmission and charging. Since it is difficult to look for a good copper core as it is mounted inside the USB cable, choose a thick and heavy cable in this sense. Similar to how people look for
Material:
Speaking of material, there are surely tons of materials being utilized in the market for USB cables. Some manufacturers often used TPE, nylon, metal weaving, or PVC.
- TPE – A type of material that is made of plastic and has a good amount of toughness and flexibility. TPE can be recycled, hence it is environment-friendly. Today, smartphone manufacturers who originally used USB cables for charging, still use this type of material.
- Nylon – This is a special kind of material used for USB cables. It enhances the peripheral tension of the cord and ensures that the inner copper core is protected against external pressures. Nylon material is pretty strong and durable and has a polished look.
- PVC – This is by far the most commonly used material for USB cables. It is non-inflammable, durable, external factor resistance, and great stability. But, TPE material aces in terms of appearance and better performance because of its outer coating material.
Which is Better, 28/28 or 28/24 Gauge?
One of the things you need to take note when looking for a good USB cable is its charging and data wires. With 28/28 gauge, the cord is using 28 AWG for both charging and data. By the way, AWG stands for American Wire Gauge, a standardized abbreviation used by manufacturers of electronics.
Now, going back, a 28/28 gauge is will charge your device slowly, which is in total contrast of 28/24 — thanks to the power of 24 AWG — as it can manage 2 amp power. The 28/28 gauge can only handle a maximum of 500 mAh which is considered to be slow charging compared to the 28/24.
As explained previously, if the amp (ampere) is higher, the electricity flow to your device is also higher. Hence, your device will charge quicker as it receives a higher flow of electricity. So, whenever you plan to look for a cord, always choose a USB cable with 28/24 gauge
Conclusion:
There are times we often opt for something cheaper, just because it look and perform the same way with expensive ones. Just like when it comes to buying USB cables. The market offers tons and they all look and work similarly, not knowing if each is made with high-quality materials. If you want something that lasts longer, and you get more than what you are paying for, then be meticulous and look for a good USB cable. The things listed above will surely help you out.
Read Also: