Caring for a loved one with diabetes is a significant responsibility that comes with various challenges, including managing the financial aspects of their healthcare. The Dexcom G6 continuous glucose monitoring system offers an advanced solution for diabetes management, but caregivers need to carefully consider the associated costs. In this article, we will explore the financial considerations that caregivers should take into account when contemplating the use of the Dexcom G6 system.
Understanding The Dexcom G6 System
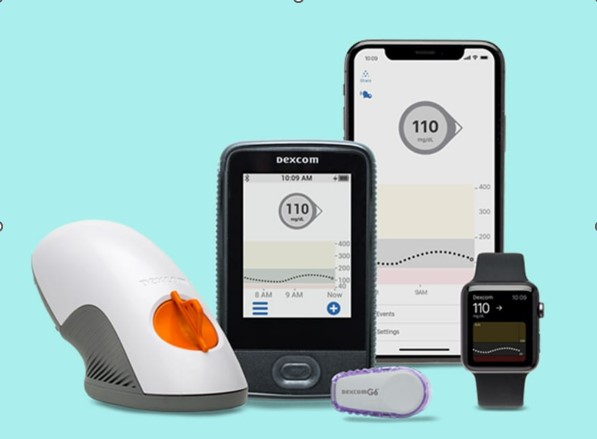
The Dexcom G6 is a revolutionary device that provides continuous glucose monitoring for individuals with diabetes. It offers real-time information about blood sugar levels, allowing for better management and timely interventions. This technology not only improves the quality of life for those with diabetes but also brings significant peace of mind to caregivers.
Initial Costs And Essential Components
When considering the Dexcom G6 system, caregivers need to factor in the initial costs. These costs include acquiring the transmitter, receiver, or compatible smartphone, as well as the sensors that attach to the skin to measure glucose levels. While the upfront expense might seem substantial, it’s crucial to view it as an investment in better diabetes management and long-term health outcomes.
Ongoing Sensor Expenses
One of the ongoing costs associated with the Dexcom G6 system is the need for sensor replacement every 10 days. This regular replacement cycle ensures accurate and reliable glucose monitoring. Caregivers should be prepared for these recurring costs and budget accordingly.
Insurance Coverage And Reimbursement
Many insurance plans provide coverage for medical devices like the Dexcom G6 system. Caregivers should thoroughly review the loved one’s insurance policy to understand the extent of coverage and the reimbursement process. Engaging in discussions with insurance providers and healthcare professionals can help clarify the financial aspect and ensure optimal coverage.
Exploring Financial Assistance Programs
Caregivers should be aware that there are financial assistance programs available to help manage the costs of the Dexcom G6 system. Research and inquire about organizations, foundations, and patient assistance programs that offer support to individuals with diabetes. These programs can provide much-needed relief from the financial burden.
Weighing Long-Term Benefits And Short-Term Costs
While the financial considerations of using the Dexcom G6 system are significant, caregivers must also evaluate the long-term benefits. Improved glucose management can lead to fewer hospitalizations, reduced complications, and enhanced overall well-being for loved ones with diabetes. Caregivers should approach the costs as an investment in long-term health outcomes.
Open Communication And Financial Planning
Transparent communication with healthcare providers is crucial for caregivers. Discussing financial concerns, insurance coverage, and available assistance programs can offer valuable insights and guidance. Healthcare professionals can help caregivers effectively integrate the Dexcom G6 system into their loved one’s diabetes management plan while taking the financial aspect into account.
Conclusion
Choosing to invest in the Dexcom G6 system involves more than just considering the financial implications; it’s about investing in the health and well-being of a loved one with diabetes. While the costs associated with the system are a legitimate concern, the potential benefits in terms of improved glucose management and enhanced quality of life cannot be overlooked. By carefully considering the Dexcom G6 cost and exploring financial assistance options, caregivers can make informed decisions that prioritize their loved one’s health and provide peace of mind for both themselves and their loved ones.
Read Also :
- Unhealthy And Healthy Solutions For Coping With Stress
- 8 Fitness Hacks That Will Make Your Life Better