Measuring the distance between two addresses is important for business and personal use.
Several methods are available for measuring the distance between two addresses, whether you’re trying to plan a delivery route, determine how far apart two properties are, or estimate your estimated arrival time for brunch.
However, with an overwhelming amount of options, the next logical question is, “which method is best for your situation?” To determine this, you will need to answer some preliminary questions, including, “Am I measuring the driving distance between two addresses or a straight line distance?” and “Am I using exact addresses, coordinates, or city names?” This article will compare the different ways of calculating the distance between two addresses.
Here Are 3 Prime Steps To Measure The Distance Between Two Addresses
1. Using GPS

The first and most basic method is GPS, which provides a great way to get a general idea of distance and travel time. GPS devices use satellite technology to determine your location and the location of other points and can provide highly accurate distance measurements.
Searchers can use GPS by entering the two addresses into the device and selecting “enter” or “go.” The result will give the inquirer the distance between the two points and the estimated travel time. However, this method can be limited in accuracy, especially if the addresses are remote or the roads are not well-mapped.
2. Google Maps
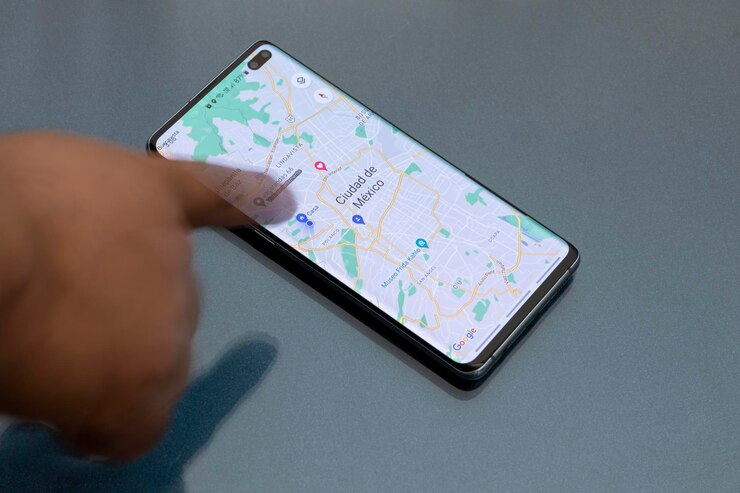
Google Maps is a convenient tool for measuring the distance between two addresses. To measure the driving distance, simply enter the addresses into the search bar and click on the “Directions” icon.
Select the “Driving” option and “Get Directions” to display the route and total distance on the map. Using this method can be helpful when planning a road trip or estimating travel time.
However, the driving distance displayed may differ from the actual mileage due to factors such as traffic and construction. Despite this, it can still be useful for measuring the driving distance between two points.
3. GIS Software
GIS (Geographic Information Systems) software is a tool that allows users to analyze and visualize geographic data.
GIS software typically includes a variety of tools for data management, spatial analysis, and mapping. GIS software can measure the distance between two locations in various ways, depending on the specific software and the available data.
Some of these ways are:
- Measuring the straight-line distance between two points is often the most straightforward method, allowing users to use the “Measure Distance” or “Distance” tool, typically found in the toolbar or menu.
- Measuring the shortest path distance between two points can be used when the data includes information about the terrain or other features that affect the distance between two locations.
- Measuring the distance along a specific route can be used when the data includes information about roads or other transportation networks and can help determine the length along a particular way, such as the distance between two addresses on a map.
The only caveat is that GIS software does not consider the terrain or other features that can affect the distance between two locations.
Making Your Choice
Before deciding, it is important to consider the type of distance measurement you need (driving or straight line) and the accuracy required before choosing a method. Weighing the pros and cons will help ensure that you are making the best decision for what you are hoping to achieve.